Flex PCB Assembly
Altest’s Corporations offer Flex PCB assembly is the process of assembling components on a flex board. This assembly process is similar to that of rigid boards.
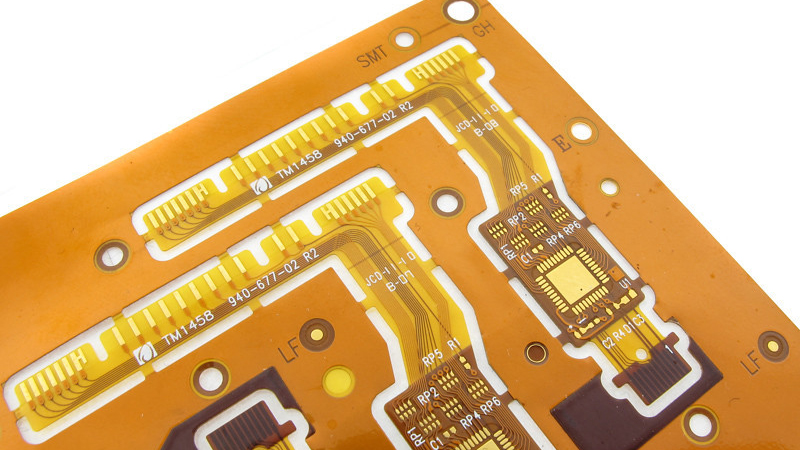
Flex PCB Assembly & manufacturer
What is a Flexible Circuit?
A flexible circuit is a printed circuit board manufactured using substrate that is naturally flexible. Flex circuits are typically manufactured using a polyimide (Kapton) material and one to multiple layers of copper. Popular suppliers of flexible materials are DuPont and Panasonic (we typically stock both). A flexible printed circuit board material will bend without snapping. However, the copper will likely crack if the bend causes a crease. A flexible circuit shouldn't be confused with a very thin "semi-flexible" FR4 board. A thin (<10 mil) FR4 board will flex, but because FR4 is brittle, will eventually snap.
What are the differences between Flex and Rigid boards?
Flexible printed circuit boards are quite different than rigid boards:
- Material; Rigid boards are typically made out of FR4 (glass-epoxy compounds) while flexible circuits are made from polyimide. There are cases when rigid boards are built with polyimide, but it isn't as common.
- Coverlay; Flex pcbs either have a flexible mask or coverlay while rigid boards typically just use a solder mask. When a coverlay is used, the openings are routed, or laser cut. Then an adhesive (typically 1 or 2 mils thick) is used to adhere the coverlay to the flex.
- Stiffeners; Flexible printed circuit boards typically use FR4 or polyimide stiffeners to stiffen specific non-flexing regions. Stiffeners are either laminated to the flex or adhered using a PSA (pressure sensitive adhesive). Rigid boards do not need stiffeners.
- Permittivity; There is a wide range of relative permittivity (dielectric constants) for rigid board materials while flexible polyimide material is typically 3.4.
What are different types of Flexible PCBs?
There are three classifications of flexible PCBs:
- Flex; A flexible pcb is a flex that could have polyimide stiffeners for zif regions, however, the overall circuit is 100% flexible.
- Flex with stiffener(s); If a flex circuit needs to be rigid in certain areas, FR4 or polyimide stiffeners can be added by lamination or PSA (pressure sensitive adhesive). Stiffeners work well for flex circuits with components only on one side.
- Rigid-flex; A rigid-flex board is a combination of a rigid board and flex circuit. The flexible layers are sandwiched between two rigid boards using no flow prepreg. This type of flex works well when there are components on both the top and bottom sides.
What are benefits of Flex PCBs?
There are many benefits to use a flexible printed circuit board in your application:
- Lightweight; Flex circuit's polyimide material is lighter than FR4.
- Thin; A typical 2-layer flex can range in thickness between 4.4 and 10 mils.
- Flexible; This is obvious, but with the ability to make bends, you have more freedom to decrease the overall mechanical footprint.
- High Temperature; Polyimide flex materials are suited for very high temperatures compared to FR4. They are also resistant to oils, gases, and acids.
